Foodborne Illness

What You Need to Know
The term foodborne illness describes any number of diseases that result from consuming contaminated food or beverages. CDC estimates that 1 in 6 Americans become sick, 128,000 are hospitalized, and 3,000 die of foodborne diseases each year.
Symptoms may differ among the different types of foodborne diseases. Common symptoms of foodborne diseases:
Although anyone can get a foodborne illness, some people are more likely to develop one. Those groups include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Stomach cramps
- Diarrhea
- Symptoms can sometimes be severe, and some foodborne illnesses can even be life-threatening.
Although anyone can get a foodborne illness, some people are more likely to develop one. Those groups include:
- Older adults
- Young children
- People with immune systems weakened from medical conditions, such as diabetes, liver disease, kidney disease, organ transplants, or HIV/AIDS, or from receiving chemotherapy or radiation treatment.
- Pregnant women
Most people with a foodborne illness get better without medical treatment, but people with severe symptoms should see their doctor.
Four Steps to Food Safety
Anyone can get sick from eating contaminated food. Follow four simple food safety steps—clean, separate, cook, and chill—to lower your chance of food poisoning and to protect yourself and your loved ones.
- Clean: Wash your hands and surfaces often
- Separate: Don't cross-contaminate
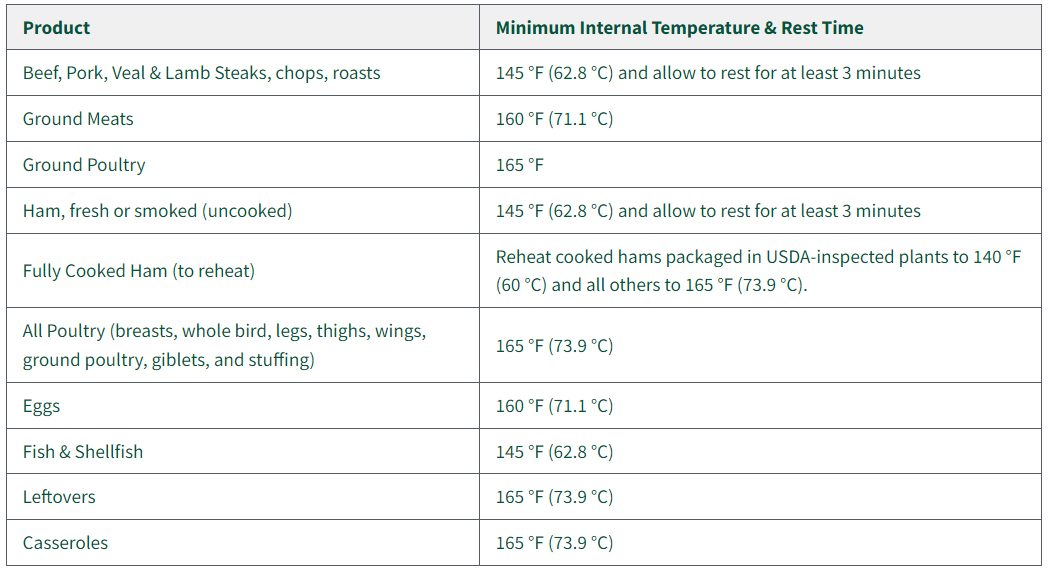
- Cook to the right temperature.
- Chill: Refrigerate promptly